在现代数据中心中,高效热管理关乎服务器稳定、能耗下降与成本优化。随着系统规模与耦合复杂度不断提升,传统“经验+规则”的方法愈发吃力。以深度强化学习(DRL)与基于学习的模型预测控制(LB-MPC)为代表的AI技术,为热管理带来新的路径。研究显示,AI驱动的动态热管理可在既有系统上进一步降低约 5%–20% 的冷却能耗。但在真实场景落地时,AI仍面临泛化、安全、样本效率、可解释、最优性与适应性等多重挑战——从“理论可行”到“可靠部署”的距离依然存在。
Read More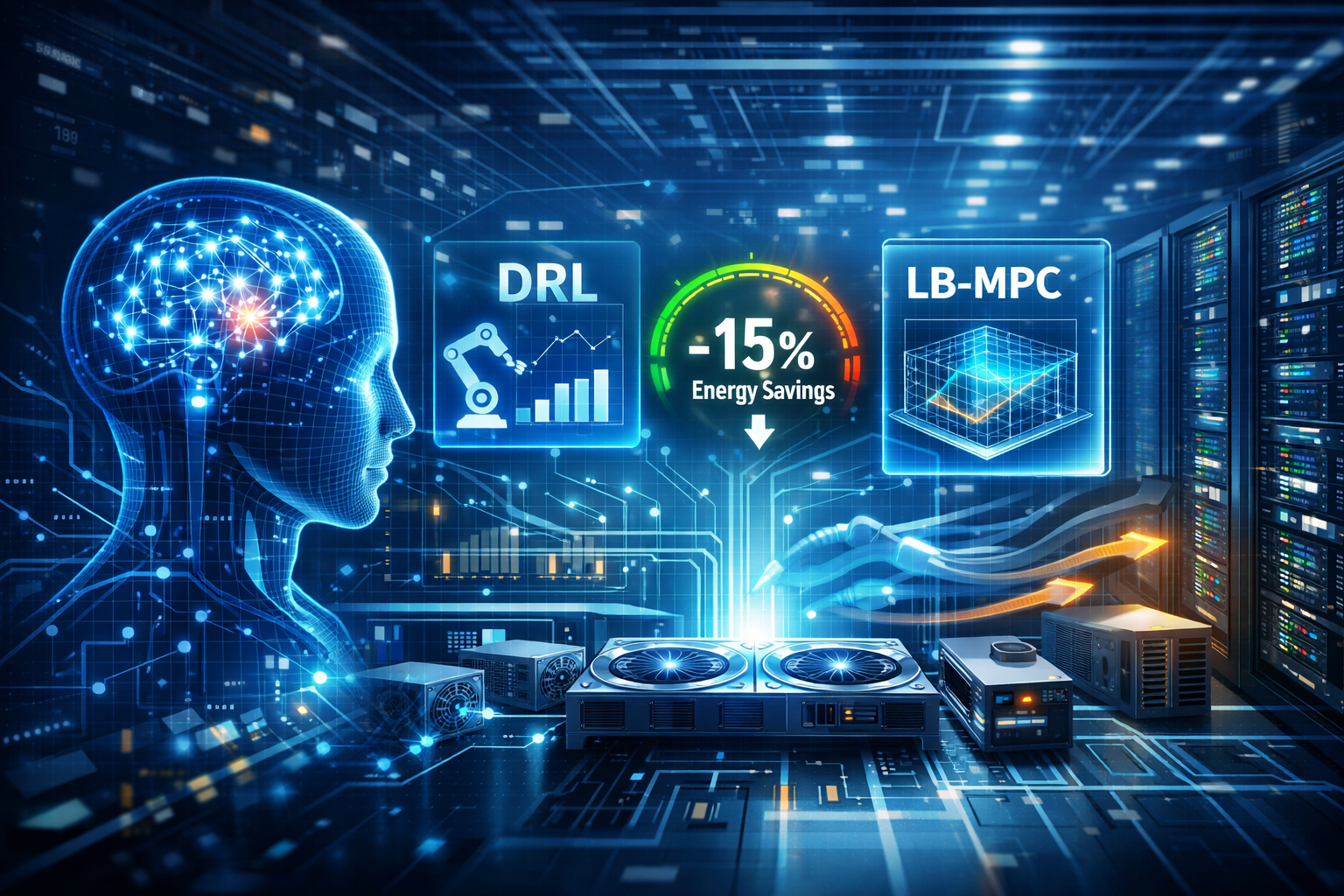


INTRODUCTION Artificial intelligence (AI) demand is rapidly expanding at an unprecedented rate all over the world. This growing trend has been piling pressure on data centers (DC). Unlike standard computational tasks, AI workloads involve complex computations for training and inference. Dedicated graphics processing unit (GPU), data processing unit (DPU), and networking devices are designed for […]
Read More
Yonggang Wen, Ph.D. As we move into 2025, the data center (DC) industry is believed to stand at the crossroads of technological innovations, environmental responsibility, and operational transformation. With the increasing demand for high-performance computing resulting from the surge in AI workloads, data centers are no longer just infrastructure providers; they have become global mission-critical […]
Read More

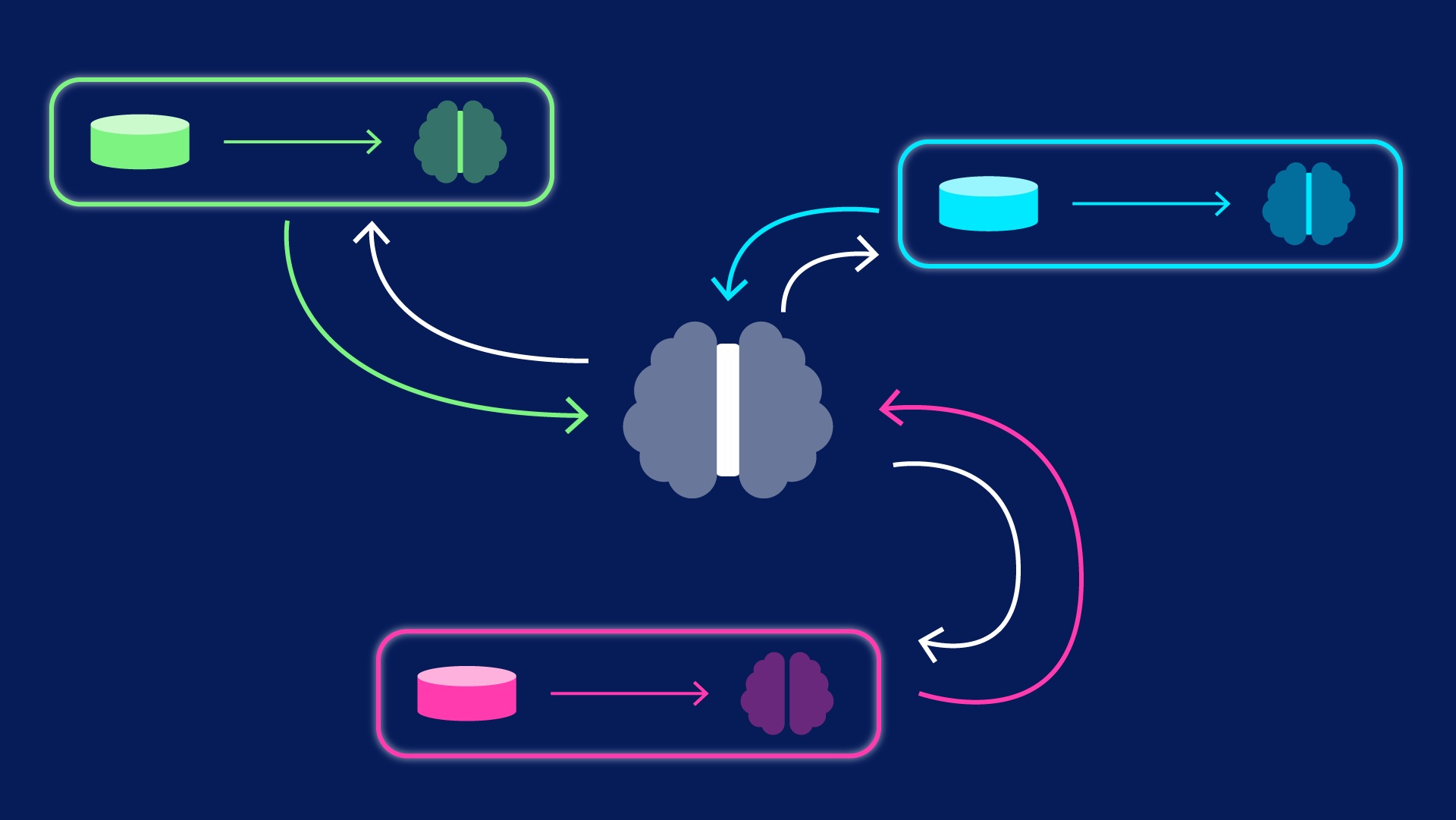
周昕 背景 基于模型的强化学习(Model-based Reinforcement Learning,MBRL)通过利用系统行为模型合成用于策略训练的的数据,被认为是解决强化学习中的高采样成本问题的一种有效方案。然而,MBRL框架受到优化控制策略、复杂目标系统的行为学习、以及复杂超参数控制等方面的限制。因此,在训练过程中往往需要大量的人工调整,成本极高。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种“强化-强化学习”(Reinforcement on Reinforcement, RoR)的结构,将复杂的MBRL任务分解成两个相互耦合的强化学习“层”。其中,内层是标准的MBRL训练过程,属于标准的马尔科夫决策过程(Markov Decision Process, MDP),被称为“训练环境”(Training Process Environment, TPE)。外层则作为强化学习的智能体,用于学习内层TPE的最佳超参数配置,被称作“智能训练器”(Intelligent Trainer),如图1所示。该方法可以灵活的为不同的MBRL训练提供优化超参数和配置服务,我们称之为“Train the trainer”,意为使用强化学习来优化强化学习的训练过程。
Read More